Links:
DKA/HHS:
Hyperglycemic Crises: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), And Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)
Inpatient Glucose Control:
American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Diabetes Association Consensus Statement on Inpatient Glycemic Control
| DKA | HHS | |
| Pathophysiology | Insulin deficiency ► mobilize fatty acids ► ketogenesis | Hyperglycemia ► osmotic diuresis ► volume depletion |
| Glucose | >250 | >600 |
| pH | <7.3 | >/= 7.3 |
| AG | Positive | Variable |
| Bicarb | <18 | >18 |
| Ketones | Positive in blood and urine | None to small |
| Serum Osm | Variable | >320 |
- Precipitants: Insulin deficiency, Iatrogenic, Infection, Inflammation, Ischemia, Infarction, Intoxication
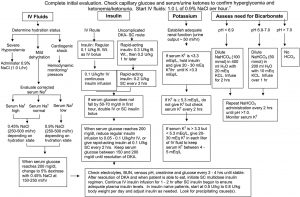
Management initial testing: CBC, CMP, Mg, Phos, serum ketones, A1c, UA, ABG, EKG, cultures (if febrile), CXR, serum Osm
calculate serum osm= 2 x Na + (glucose/18) + (BUN/2.8)
calculate corrected Na = measured Na + 0.016 x (glucose- 100)
labs: Q1hr glucose, Q2-4hr BMP
algorithms as below (per UpToDate)
Protocol for management of adult patients with DKA